You might have heard these words many times, “Data is the new Oil” or “Data is the new Gold.” Everybody is behind the data. You might have seen several times that big companies like Facebook, Twitter, Google, and many others companies being sued on data stealing charges. The globe is so mad about the data that it led to the creation of more than 4k broking firms in the globe. According to research Data broker’s market has grown to the worth of $200 billion annually. These lucrative numbers have made the birth of information-stealing software, in other words, information-stealing malware. We will explore one such information-stealing malware, which is quite popular these days, Mystic Stealer Malware.
Mystic Stealer is a relatively new information-stealing malware that can cause significant damage to its victims. First advertised in April 2023, it compromises user security and privacy by pilfering sensitive data such as credentials, browsing history, and cryptocurrency wallet information from its victims. According to security researchers from InQuest and Zscaler, the malware is found targeting nearly 40 web browsers and over 70 browser extensions. This large attack surface gives the edge for the stealer malware to steal information and send it to their C2 server.
It is much recommended to secure your information from the leak. To protect your information from Mystic Stealer, it’s essential to adopt strong cybersecurity practices. One of the most effective ways to remove this malware is by using a reputable anti-malware tool that scans and eradicates the threat automatically. Following the general security guidelines like regular software updates and safe online behavior can help you protect your information from Mystic Stealer Malware.
What is an Information Stealing Malware?
Information stealing malware, as the name suggests, is a type of malicious software (malware) designed to collect data from the victim’s machines and send it to the attacker.
These kinds of malware are used for a variety of purposes, but they’re most commonly used for identity theft, financial theft, steal sensitive information, or corporate espionage. Generally, the data they target can include personal information, such as names, addresses, and social security numbers; financial information, like credit card numbers or banking credentials; and sensitive corporate data or intellectual property.
Information-stealing malware can come in many forms, from Trojans and spyware to more sophisticated types of malware like advanced persistent threats (APTs). They can be spread through a variety of means, including email attachments, malicious downloads, or infected websites.
Understanding Mystic Stealer Malware
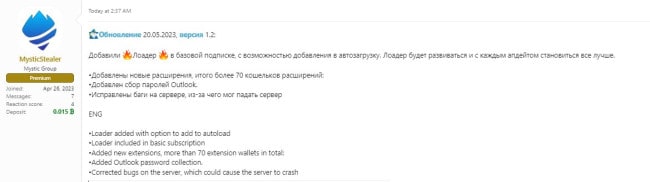
Figure 1: MysticStealer forum post advertising v1.2 update with loader support (Source: Inquest)
Mystic Stealer is a type of malware that primarily focuses on stealing information. First advertised in the underground economy in April 2023, this malware is noted for its data theft capabilities, code obfuscation techniques, and use of an encrypted binary protocol to evade detection. Some of the information it can extract from infected systems includes:
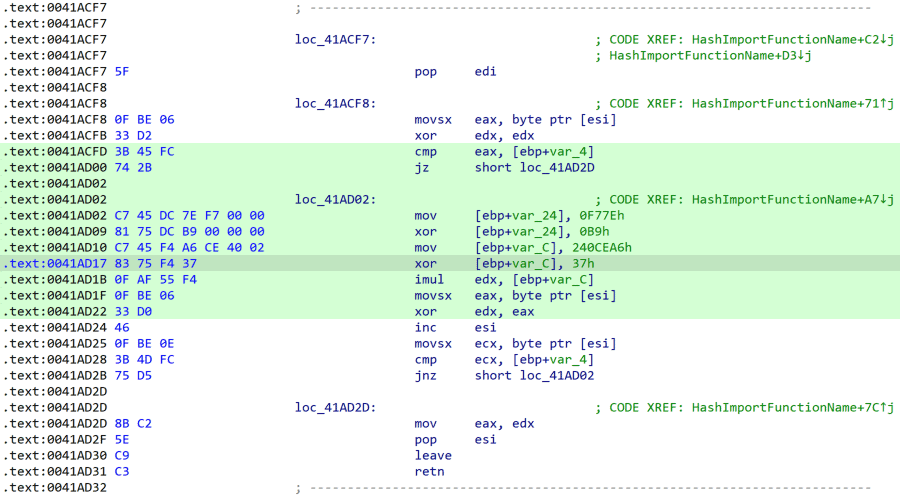
Figure 2: Example Mystic Stealer constant obfuscation technique (Source: Inquest)
- System information such as the hostname, user name, GUID, keyboard layout, locale, CPU information, number of CPU processors, screen dimensions, computer name, username, running processes, system architecture, and operating system version.
- Auto-fill data, browsing history, cookies, and stored credentials from nearly 40 different web browsers.
- Data related to installed cryptocurrency wallets.
- Credentials for platforms like Telegram and Steam.
- Arbitrary files.
Mystic Stealer is implemented in C for the client and Python for the control panel. It does not require third-party libraries for decrypting or decoding target credentials, which makes it different from many leading stealers. Instead, Mystic Stealer collects and exfiltrates information from an infected system and then sends the data to a command & control (C2) server that handles parsing.
On May 20, the Mystic Stealer seller posted updates that include loader functionality and a persistence capability, allowing the malware to download and execute additional payloads1. The malware also has several anti-analysis and evasion features such as:
- Binary expiration: The trojan will terminate execution if the running build is older than a specified date.
- Anti-virtualization: Some samples contain anti-VM features, detecting hypervisor runtime environments, and avoiding execution.
- Windows APIs imported by hash: The stealer resolves and dynamically loads Windows APIs using a custom XOR-based hashing algorithm.
- Dynamic constant calculation: Constant values in the code are obfuscated and dynamically calculated at runtime.
- Encrypted binary custom protocol: The client communicates with the C2 server using a custom protocol over TCP.
- Polymorphic string obfuscation: The malware obfuscates strings using a library that is very similar to ADVobfuscator, making it more difficult for antivirus software to detect the malware.

Figure 3: Mystic Stealer control panel builder dialog (Source: Inquest)
Mystic Stealer communicates with its C2 servers using a custom binary protocol over TCP. The client sends a hello message containing a constant 4 byte value to the C2 server, which responds with 256 bytes of binary data that is used as an RC4 key for all subsequent communications. The client then encrypts and sends various system information to the C2 server. Unlike most stealers, Mystic Stealer does not store or write data to the disk, which may make it less detectable by antivirus applications. The builder of Mystic Stealer allows operators to specify up to four C2 endpoints, providing resiliency in case some servers are offline or blocklisted.
Full technical details are available here. Please don’t forget to visit for full analysis.
Indicators of Compromise
IOCs captured during analysis.
C2 Server Endpoints
- 194[.]169.175.123:13219
- 185[.]252.179.18:13219
- 142[.]132.201.228:13219
- 135[.]181.47.95:13219
- 94[.]130.164.47:13219
- 94[.]23.26.20:13219
- 91[.]121.118.80:13219
Targeted Web Browsers
- Opera
- K-Meleon
- Mozilla icecat
- Mozilla Firefox
- Comodo IceDragon
- 8pecxstudios Cyberfox
- NETGATE Technologies BlackHawk
- Torch
- Chedot
- Kometa
- liebao
- Comodo
- Iridium
- Vivaldi
- Orbitum
- K-Melon
- Chromium
- QIP Surf
- Maxthon3
- Nichrome
- Chromodo
- Amigo
- 7Star
- CentBrowser
- Mail.Ru Atom
- Google Chrome
- Coowon
- uCozMedia Uran
- CocCoc Browser
- Microsoft Edge
- Sputnik
- Elements Browser
- 360Browser
- Epic Privacy Browser
- CatalinaGroup Citrio
- YandexBrowser
- MapleStudio ChromePlus
- Brave-Browser
- Fenrir Inc Sleipnir5 ChromiumViewer
Targeted MFA and Cryptocurrency Wallet Browser Extensions
| Extension ID | Browser Extension Name |
| Ibnejdfjmmkpcnlpebklmnkoeoihofec | TronLink |
| fhbohimaelbohpjbbldcngcnapndodjp | BinanceChain |
| ffnbelfdoeiohenkjibnmadjiehjhajb | Yoroi |
| jbdaocneiiinmjbjlgalhcelgbejmnid | Nifty Wallet |
| afbcbjpbpfadlkmhmclhkeeodmamcflc | Math Wallet |
| hnfanknocfeofbddgcijnmhnfnkdnaad | Coinbase Wallet |
| hpglfhgfnhbgpjdenjgmdgoeiappafln | Guarda |
| blnieiiffboillknjnepogjhkgnoapac | EQUAL Wallet |
| cjelfplplebdjjenllpjcblmjkfcffne | Jaxx Liberty |
| fihkakfobkmkjojpchpfgcmhfjnmnfpi | BitApp Wallet |
| kncchdigobghenbbaddojjnnaogfppfj | iWallet |
| amkmjjmmflddogmhpjloimipbofnfjih | Wombat |
| nlbmnnijcnlegkjjpcfjclmcfggfefdm | MEW CX |
| nanjmdknhkinifnkgdcggcfnhdaammmj | GuildWallet |
| nkddgncdjgjfcddamfgcmfnlhccnimig | Saturn Wallet |
| fnjhmkhhmkbjkkabndcnnogagogbneec | Ronin Wallet |
| cphhlgmgameodnhkjdmkpanlelnlohao | NeoLine |
| nhnkbkgjikgcigadomkphalanndcapjk | Clover Wallet |
| kpfopkelmapcoipemfendmdcghnegimn | Liquality Wallet |
| aiifbnbfobpmeekipheeijimdpnlpgpp | Terra Station |
| dmkamcknogkgcdfhhbddcghachkejeap | Keplr |
| fhmfendgdocmcbmfikdcogofphimnkno | Sollet |
| cnmamaachppnkjgnildpdmkaakejnhae | Auro Wallet |
| jojhfeoedkpkglbfimdfabpdfjaoolaf | Polymesh Wallet |
| flpiciilemghbmfalicajoolhkkenfel | ICONex |
| nknhiehlklippafakaeklbeglecifhad | Nabox Wallet |
| hcflpincpppdclinealmandijcmnkbgn | KHC |
| ookjlbkiijinhpmnjffcofjonbfbgaoc | Temple |
| mnfifefkajgofkcjkemidiaecocnkjeh | TezBox |
| lodccjjbdhfakaekdiahmedfbieldgik | DAppPlay |
| Ijmpgkjfkbfhoebgogflfebnmejmfbml | BitClip |
| lkcjlnjfpbikmcmbachjpdbijejflpcm | Steem Keychain |
| nkbihfbeogaeaoehlefnkodbefgpgknn | MetaMask |
| bcopgchhojmggmffilplmbdicgaihlkp | Hycon Lite Client |
| klnaejjgbibmhlephnhpmaofohgkpgkd | ZilPay |
| aeachknmefphepccionboohckonoeemg | Coin98 Wallet |
| bhghoamapcdpbohphigoooaddinpkbai | Authenticator |
| dkdedlpgdmmkkfjabffeganieamfklkm | Cyano Wallet |
| nlgbhdfgdhgbiamfdfmbikcdghidoadd | Byone |
| onofpnbbkehpmmoabgpcpmigafmmnjhl | Nash Extension |
| cihmoadaighcejopammfbmddcmdekcje | Leaf Wallet |
| gaedmjdfmmahhbjefcbgaolhhanlaolb | Authy 2FA |
| oeljdldpnmdbchonielidgobddffflal | EOS Authenticator |
| ilgcnhelpchnceeipipijaljkblbcobl | GAuth Authenticator |
| imloifkgjagghnncjkhggdhalmcnfklk | Trezor Password Manager |
| infeboajgfhgbjpjbeppbkgnabfdkdaf | OneKey |
| cgeeodpfagjceefieflmdfphplkenlfk | EVER Wallet |
| pdadjkfkgcafgbceimcpbkalnfnepbnk | KardiaChain Wallet |
| acmacodkjbdgmoleebolmdjonilkdbch | Rabby Wallet |
| bfnaelmomeimhlpmgjnjophhpkkoljpa | Phantom |
| fhilaheimglignddkjgofkcbgekhenbh | Oxygen – Atomic Crypto Wallet |
| mgffkfbidihjpoaomajlbgchddlicgpn | Pali Wallet |
| hmeobnfnfcmdkdcmlblgagmfpfboieaf | XDEFI Wallet |
| lpfcbjknijpeeillifnkikgncikgfhdo | Nami |
| dngmlblcodfobpdpecaadgfbcggfjfnm | MultiversX DeFi Wallet |
| bhhhlbepdkbapadjdnnojkbgioiodbic | Solflare Wallet |
| jnkelfanjkeadonecabehalmbgpfodjm | Goby |
| jhgnbkkipaallpehbohjmkbjofjdmeid | SteemKeychain |
| jnlgamecbpmbajjfhmmmlhejkemejdma | Braavos Smart Wallet |
| kkpllkodjeloidieedojogacfhpaihoh | Enkrypt: Ethereum, Polkadot & RSK Wallet |
| mcohilncbfahbmgdjkbpemcciiolgcge | OKX Wallet |
| gjagmgiddbbciopjhllkdnddhcglnemk | Hashpack |
| kmhcihpebfmpgmihbkipmjlmmioameka | Eternl |
| phkbamefinggmakgklpkljjmgibohnba | Pontem Aptos Wallet |
| lpilbniiabackdjcionkobglmddfbcjo | Keeper Wallet |
| cjmkndjhnagcfbpiemnkdpomccnjblmj | Finnie |
| aijcbedoijmgnlmjeegjaglmepbmpkpi | Leap Terra Wallet |
| fdjamakpfbbddfjaooikfcpapjohcfmg | Dashlane — Password Manager |
| fooolghllnmhmmndgjiamiiodkpenpbb | NordPass® Password Manager & Digital Vault |
| pnlccmojcmeohlpggmfnbbiapkmbliob | RoboForm Password Manager |
| hdokiejnpimakedhajhdlcegeplioahd | LastPass: Free Password Manager |
| naepdomgkenhinolocfifgehidddafch | Browserpass |
| bmikpgodpkclnkgmnpphehdgcimmided | MYKI Password Manager & Authenticator |
| efbglgofoippbgcjepnhiblaibcnclgk | Martian Wallet for Sui & Aptos |
Targeted Cryptocurrency Applications
- MyMonero
- Exodus
- Binance
- Raven
- Armory
- Dogecoin
- MultiBit
- Bitcoin
- DashCore
- Electrum
- Litecoin
- BitcoinGold
- WalletWasabi
- Atomic
- Guarda
- Electrum-LTC
- MyCrypto
- Bisq
- DeFi Blockchain
- Coinomi
- TokenPocket
Please visit these Git pages for updated IOCs.
- Mystic Stealer C2 servers
- Domains observed in the Grand cluster
- Grand cluster domain nameservers
- Grand domain cluster WHOIS sample
Attack Vector of Mystic Stealer Malware
Like any other malware, Mystic Stealer uses these common attack vectors to infect the victim host.
Phishing Emails
One common method of infection for Mystic Stealer malware is phishing emails. Cybercriminals craft deceptive emails designed to entice recipients into clicking on malicious links or opening attachments containing malware. These emails often appear to be from legitimate sources and may use convincing language urging the target to take action. To protect oneself, it is important to be vigilant and cautious when opening emails from unfamiliar senders or with suspicious content.
Malicious Websites
Another method of infection is through malicious websites. Cybercriminals create websites containing the Mystic Stealer malware and use various techniques such as malvertising, or inserting ads with malicious code, to lure unsuspecting users onto the site. Once the user visits the site, the malware can exploit vulnerabilities in the user’s browser or system to infect their computer. To avoid infection from malicious websites, it’s wise to have reputable antivirus software installed and updated and be cautious when visiting unfamiliar websites or clicking on suspicious links.
Software Vulnerabilities
Mystic Stealer malware can also infiltrate systems by exploiting software vulnerabilities. Outdated or unpatched software with known security flaws creates an opportunity for cybercriminals to introduce malware into a user’s computer. Regularly updating software and applying security patches can help protect against this method of infection. In addition to keeping software up to date, it’s also beneficial to have a strong security suite in place that can detect and remove any malware threats, including Mystic Stealer.
How You Should Detect that You Are Infected with Mystic Stealer Malware?
Unusual System Behavior
Detecting Mystic Stealer malware requires vigilance in monitoring for unusual system behavior. The malware typically exhibits signs of data theft, including collecting computer information such as the system’s hostname, user name, and GUID. Additionally, Mystic Stealer identifies a likely system user geolocation using the locale and keyboard layout1. Users should watch out for these indicators and report any suspicious signs to their IT department or cybersecurity professional.
Antivirus Scanning
Another essential element in detecting Mystic Stealer is frequent antivirus scanning. The malware has a low detection rate, as it employs code manipulation techniques to evade detection by most antivirus products2. However, conducting regular antivirus scans on your system can help improve the chances of identifying Mystic Stealer or any other malicious software.
To further enhance your protection against Mystic Stealer, ensure that your antivirus software is up-to-date and capable of flagging suspicious activities on your system. It is also recommended to complement antivirus scanning with other security tools such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and endpoint security solutions.
References
- https://inquest.net/blog/2023/06/15/mystic-stealer-new-kid-block
- https://www.cyfirma.com/outofband/mystic-stealer-evolving-stealth-malware/
Ways to Prevent Mystic Stealer Malware
Regular Software Updates
To protect your information from Mystic Stealer malware, it is crucial to regularly update the software on all devices. This includes operating systems, browsers, and other applications. Updates often come with security patches that fix known vulnerabilities, which can prevent malware from infiltrating your system. Set your devices to update automatically whenever possible, and keep an eye out for available updates by manually checking the developers’ websites.
Strong Password Practices
Implementing strong password practices is another important step in safeguarding your information. Create complex, unique passwords for each of your accounts, combining upper- and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. Avoid using easily guessable information, such as names or birthdays. Additionally, consider using a reputable password manager to securely store and manage your passwords. It’s also essential to change your passwords periodically, especially for sensitive accounts, to further reduce the risk of unauthorized access.
Firewall and Antivirus Protection
Implementing firewall and antivirus protection is an effective way to minimize the risk of Mystic Stealer malware. Firewalls act as a barrier between your devices and the internet, blocking unauthorized access while allowing safe traffic to pass through. Configure your firewall settings according to your specific needs, and regularly monitor its logs to identify any potential threats.
Make sure to also install reputable antivirus software on all your devices, which can detect, quarantine, and remove malware before it infiltrates your system. Keep your antivirus software up to date, and run regular scans to ensure your device remains free from malicious threats.
By taking these preventive measures, you can significantly reduce the likelihood of your information being compromised by Mystic Stealer malware.
How to Respond to a Mystic Stealer Infection?
Mystic Stealer is a dangerous malware that can compromise the security and privacy of individuals and organizations by stealing sensitive information such as credentials, browsing history, and cryptocurrency wallet data. In the event of a Mystic Stealer infection, follow these steps to mitigate the damage and protect your information.
Isolate and Disconnect
As soon as you suspect a Mystic Stealer infection, it’s crucial to act quickly to prevent further damage. First, isolate the infected device from any networks it’s connected to, such as Wi-Fi or Ethernet cables, to stop the malware from spreading to other devices or communicating with its command and control server. Disconnect any external devices or peripherals, as these may also be affected.
Remove the Malware
Once the infected device is isolated and disconnected, proceed with removing the Mystic Stealer malware. Use reputable antivirus software capable of detecting and eliminating the threat. Follow the antivirus software’s guidelines for removing the malware and avoid using the device until the malware has been completely removed. If necessary, consult with a professional in malware removal or your organization’s IT department for assistance.
Recovery and Reporting
After successfully removing the Mystic Stealer malware, it’s time to focus on recovery and reporting. Restore any affected data from secure backups, ensuring they were created before the infection occurred. Run thorough scans on restored files and devices to ensure they are malware-free.
Report the incident to relevant authorities, such as local law enforcement or regulatory bodies, if sensitive data or financial information was compromised. Additionally, notify any affected individuals or organizations so they can take necessary precautions to protect their information. It’s crucial to stay proactive in order to prevent future infections—regularly update and patch your devices, always use reputable antivirus software, and apply best practices for browsing and downloading files online.



